The entry into operation of the second generation system in the General State Administration was accompanied by a package of provisions, needed to provide this system with legal cover:
- Order of the Ministry of Economy and Finance of 1 February 1996, adopting the Accounting System Instruction for the General State Administration. Later, a new Accounting Instruction was adopted by Order HAC/1300/2002, of 23 May.
- Order of the Ministry of Economy and Finance of 1 February 1996, adopting the Accounting System Instruction to be followed in the execution of State expenditure, subsequently amended by Order HAC/1299/2002, of 23 May.
- Order of the Ministry of Economy and Finance of 27 December 1995, on procedures for the payment of liabilities of the General State Administration, subsequently partially repealed by way of the Order of the Ministry of the Presidency of 19 June 2002.
- Order of the Ministry of Economy and Finance of 1 February 1996, adopting the accounting documents to be used by the General State Administration, subsequently amended by way of Order HAC/1299/2002, of 23 May.
- Order of the Ministry of Economy and Finance of 1 February 1996, adopting the Accounting Instruction for the Institutional Administration of the State.
The centralization carried out in 2000 in the architecture of the second generation system for the General State Administration was also accompanied by the respective legislative support:
- Royal Decree 578/2001, of 1 June, regulating the general principles of the General State Administration accounting information system, which repeals Royal Decree 324/1986, of 10 February, which implemented a new accounting information system in the General State Administration.
Later, in the first half of this decade, a legislative development took place with a view to facilitating electronic processing:
- Order PRE/3662/2003, of 29 December, regulating the new procedure for collecting non-tax revenues.
- Resolution of the Government Comptroller's Office of 22 October 2004, regulating access and capture of ARs by Administrative Units.
- Resolution of the Government Comptroller's Office of 15 December 2004, regulating the procedure and sending of accounting documents and supporting documentation to the Court of Auditors.
- Resolution of the Government Comptroller's Office of 28 November 2005, regulating the procedures for the processing of accounting documents in electronic file format.
- Joint Resolution of the Government Comptroller's Office and Directorate General of the Treasury and Financial Policy, of 18 February 2008, authorizing the issue of revenue documents.
This recent legislative development is the forerunner of a new generation accounting information system (SIC'3), which was first implemented in April 2009 for AGE expenditure accounting, while the implementation of revenue and treasury accounting, for this same area, is planned for early 2010, paving the way for its subsequent implementation in autonomous bodies.
Implementation of the SIC'3 expenditure phase at the AGE was preceded by the approval of the following regulations:
- Order EHA/818/2009, of 27 March, amending the Order of 1 February 1996, approving the accounting documents to be used by the General State Administration.
- Resolution of the Government Comptroller's Office of 18 March 2009, amending that of 22 September 2008, approving the specific expenditure proposal subsystem accounting documents.
In the General State Administration, in accordance with the adjoining chart, the following act as the system's Accounting Offices:
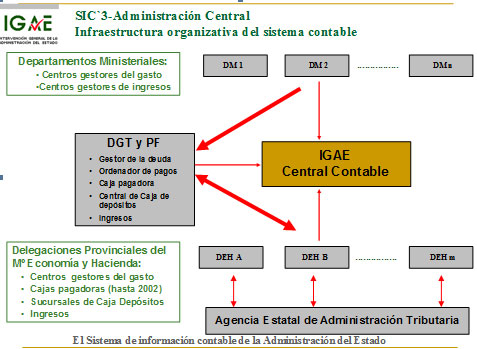
- The Accounting Offices of Ministries, at the Branch Audit Offices (except the Ministry of Defence), and the Subdirectorate General of Accounting of this Ministry.
- The Accounting Offices of Ministry of Economy and Finance Branch Offices, in the Local Audit Offices.
- The Accounting Office of the Directorate General of the Treasury and Financial Policy.
- The Central Accounting Office.
| Accounting Offices | No Offices |
|---|
| Branch Audit Offices in Ministries | 17 |
| Local Audit Offices in Ministry of Economy and Finance Branch Offices | 56 |
| Directorate General of the Treasury and Financial Policy | 1 |
| Central Accounting Office | 1 |
|
TOTAL State Administration |
75 |
The structure of the accounting information system (SIC'3) consists of a core of budgetary and economic-asset accounting and of accounting operations, together with the management of third parties, thereby forming a set of modules or applications for:
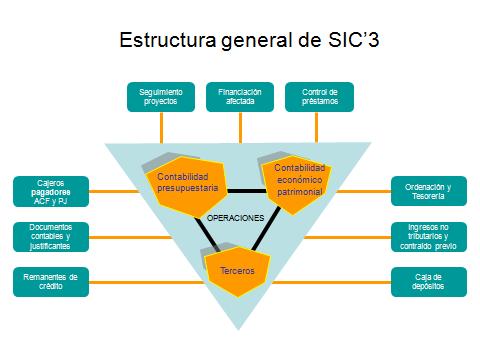
- Monitoring of the economic and budgetary management of: the supporting accounts and invoices of the paying tellers; expenditure proposals; loan control; control of expenditures with earmarked funding.
- Management within the scope of the system: payments and treasury planning; collection management of non-tax revenues and previously assumed liabilities; management and accounting of the General Deposit Fund and its branches.
- General and ancillary: accounting documents and associated supporting documentation and control of loan carry-over funds.
The system is oriented towards the manager and decision-making, so that, besides serving to cover outputs of information of a regulatory nature (annual accounts and periodic statistics), it provides the required information about:
- Budgetary execution of the expenditure management centres at any level, whether organic (who makes the expenditure), economic (what the expenditure is on) or functional (what the expenditure is for).
- The budgetary and material execution of proposed expenditures.
- The credit position of third parties with regard to the Administration.
- Preparation of the Income Budget at any level, whether organic (who makes the payment), in Public Bodies only, or economic (kind of payment). It is also possible to collect information from the taxpayer making a given payment.
- The balance in asset accounting terms.
The centralized computer architecture of the accounting information system (SIC'3) has the following characteristics:
- Three-layer J2EE and Java architecture, based on web technology.
- JDeveloper, HTML and Javascript development environment; Oracle PL/SQL and Report Builder.
- iAS applications server.
- ORACLE database under UNIX operating system.
- Access controlled through the Budget Administration Intranet; the Administrative Intranet (or, failing this, the Internet).